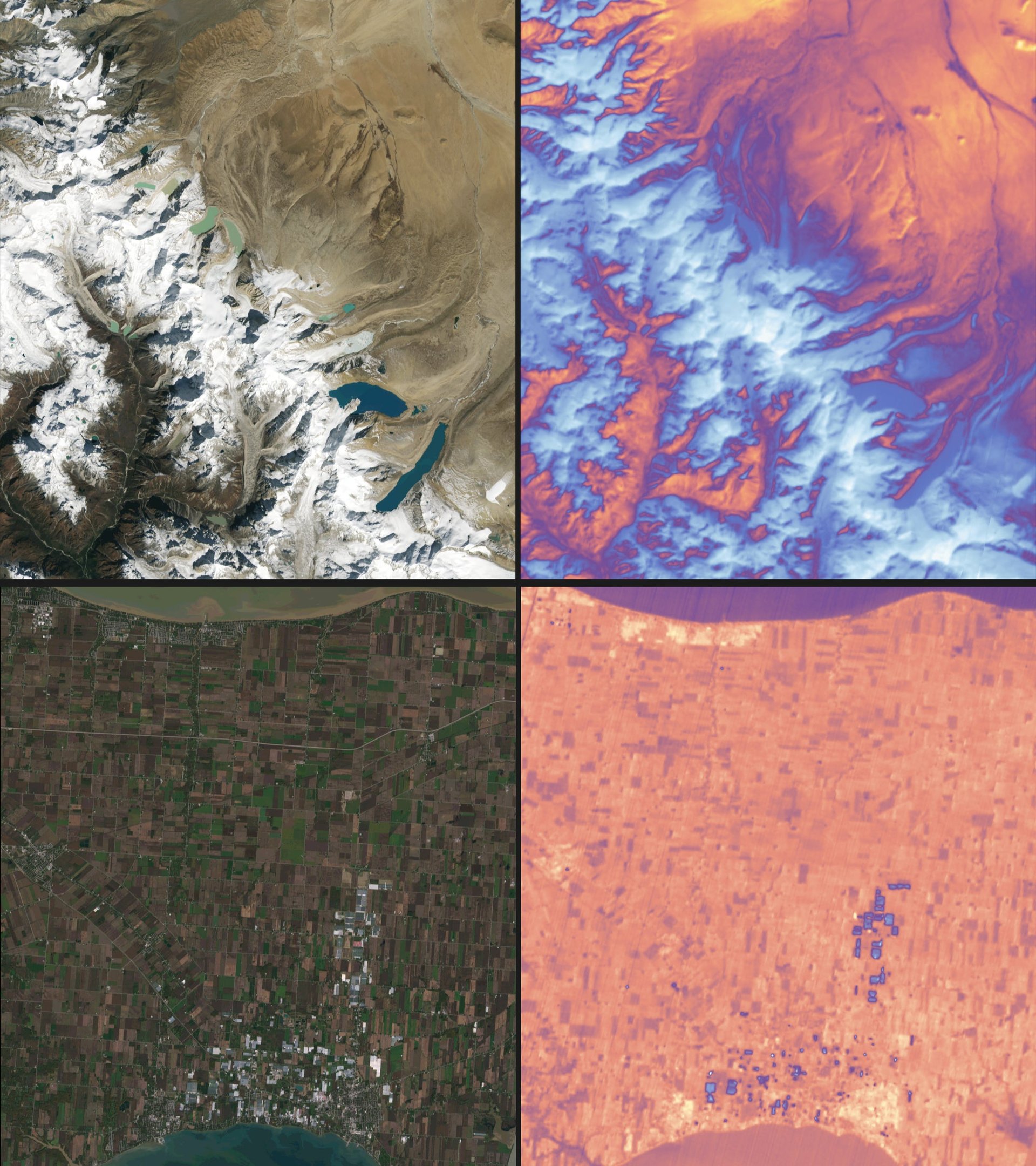
These are the first images from Landsat 9
The latest photos from space provide unparalleled views of how world’s surface is changing.


The latest photos from space provide unparalleled views of how world’s surface is changing.
Landsat 9, an Earth observation satellite that NASA launched Sept. 7, released the first photos of planet Earth captured on Oct. 31, NASA and the US Geological Survey (USGS) announced Friday (Nov. 5).
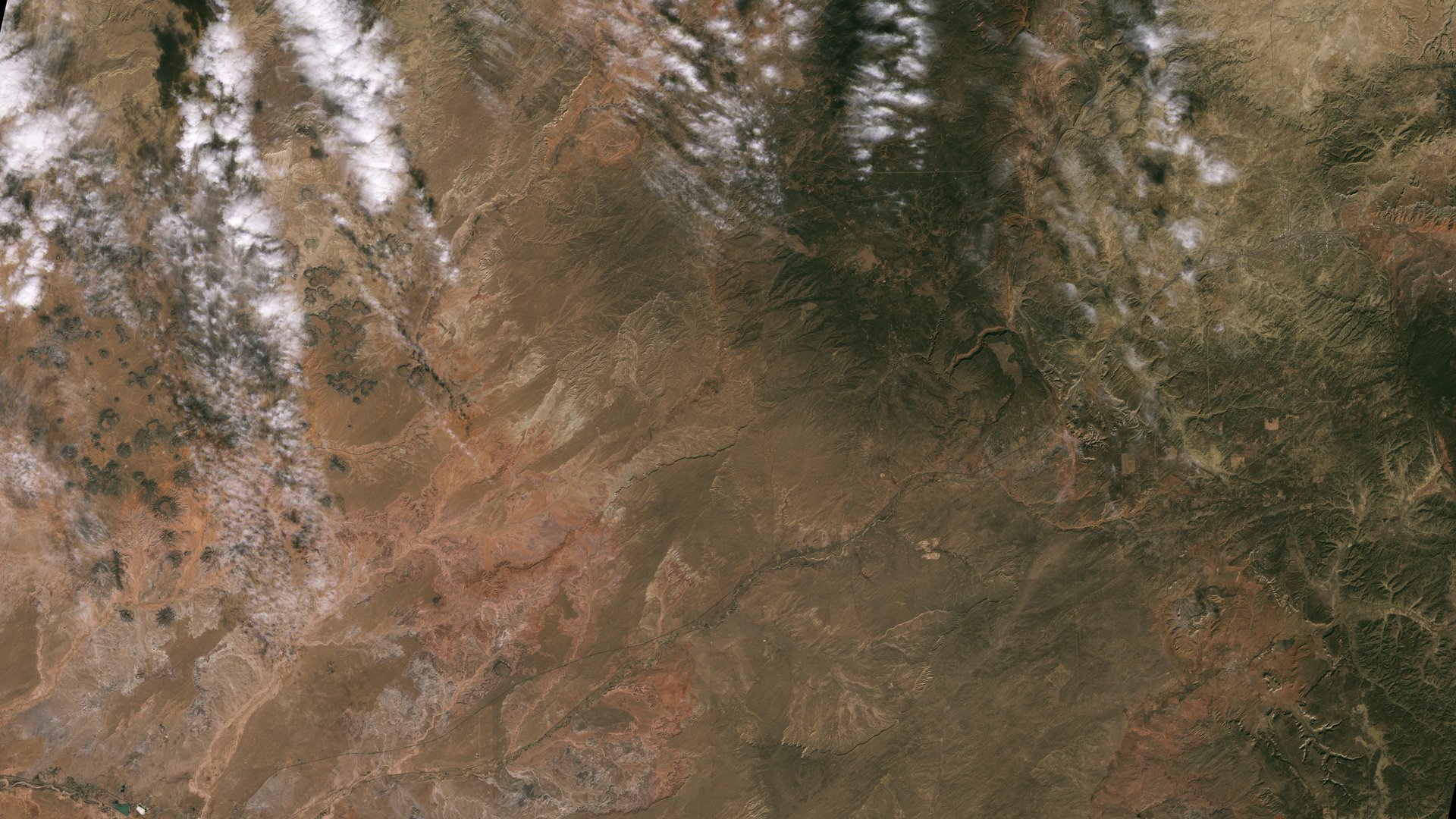
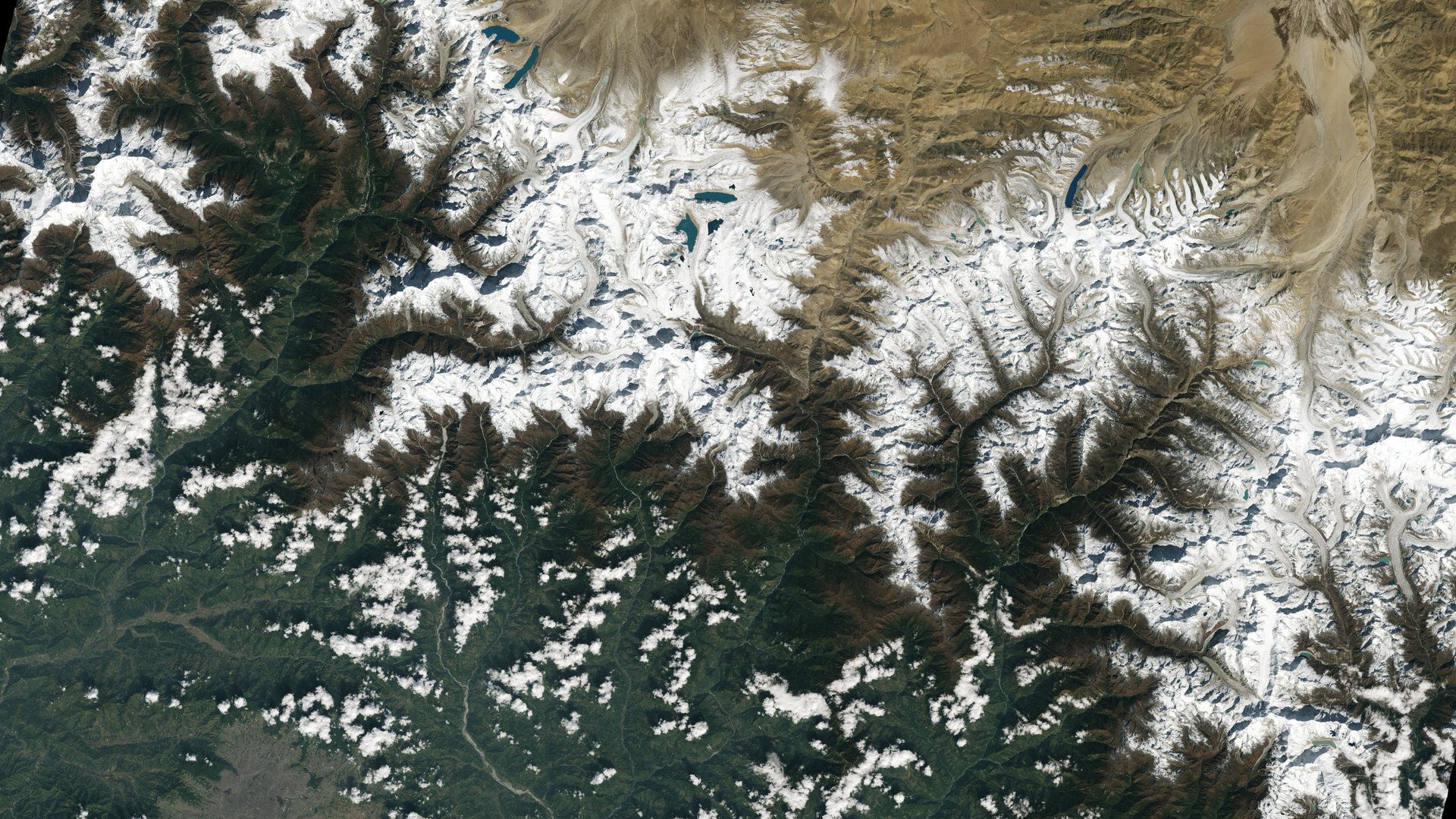
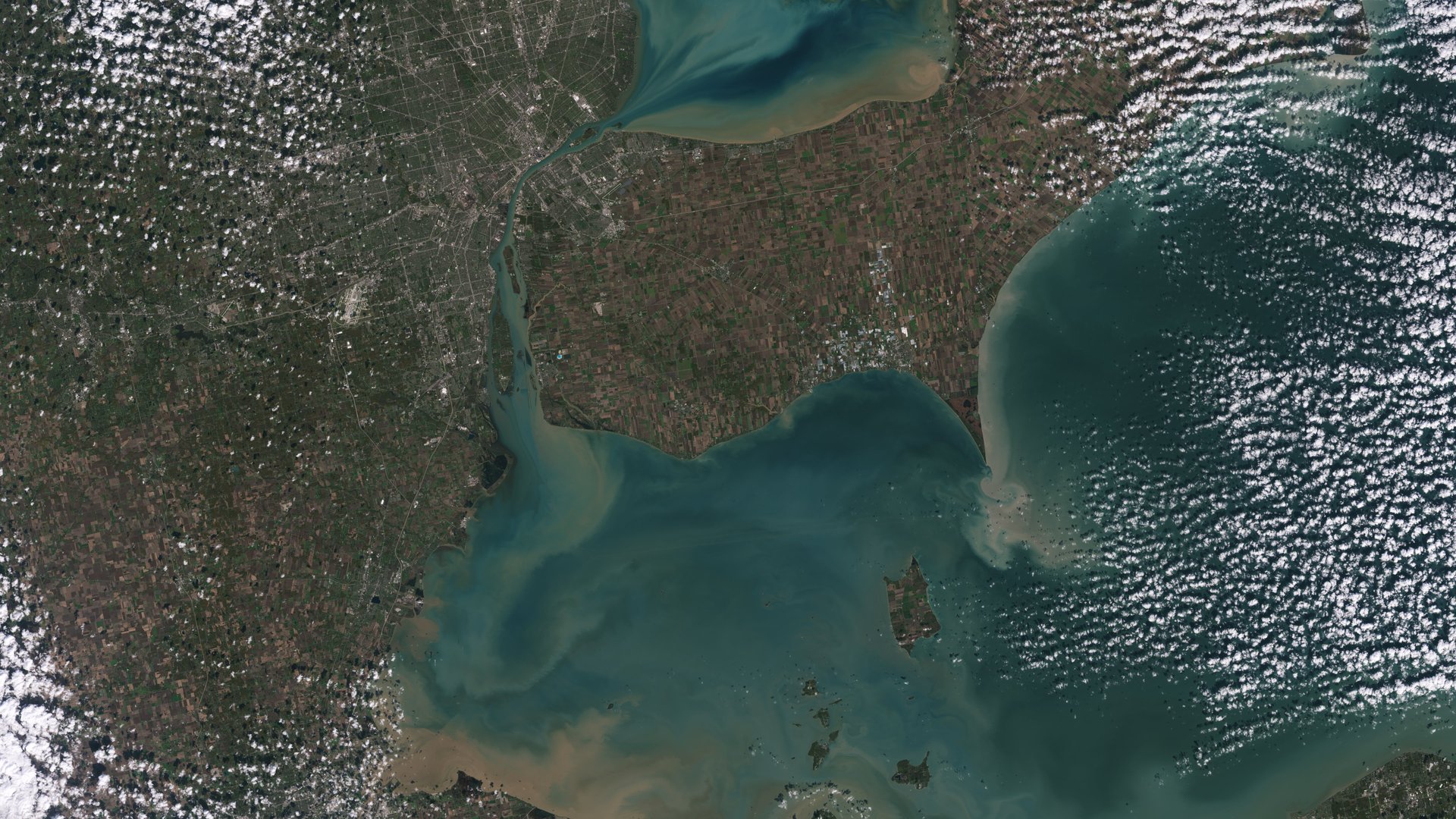
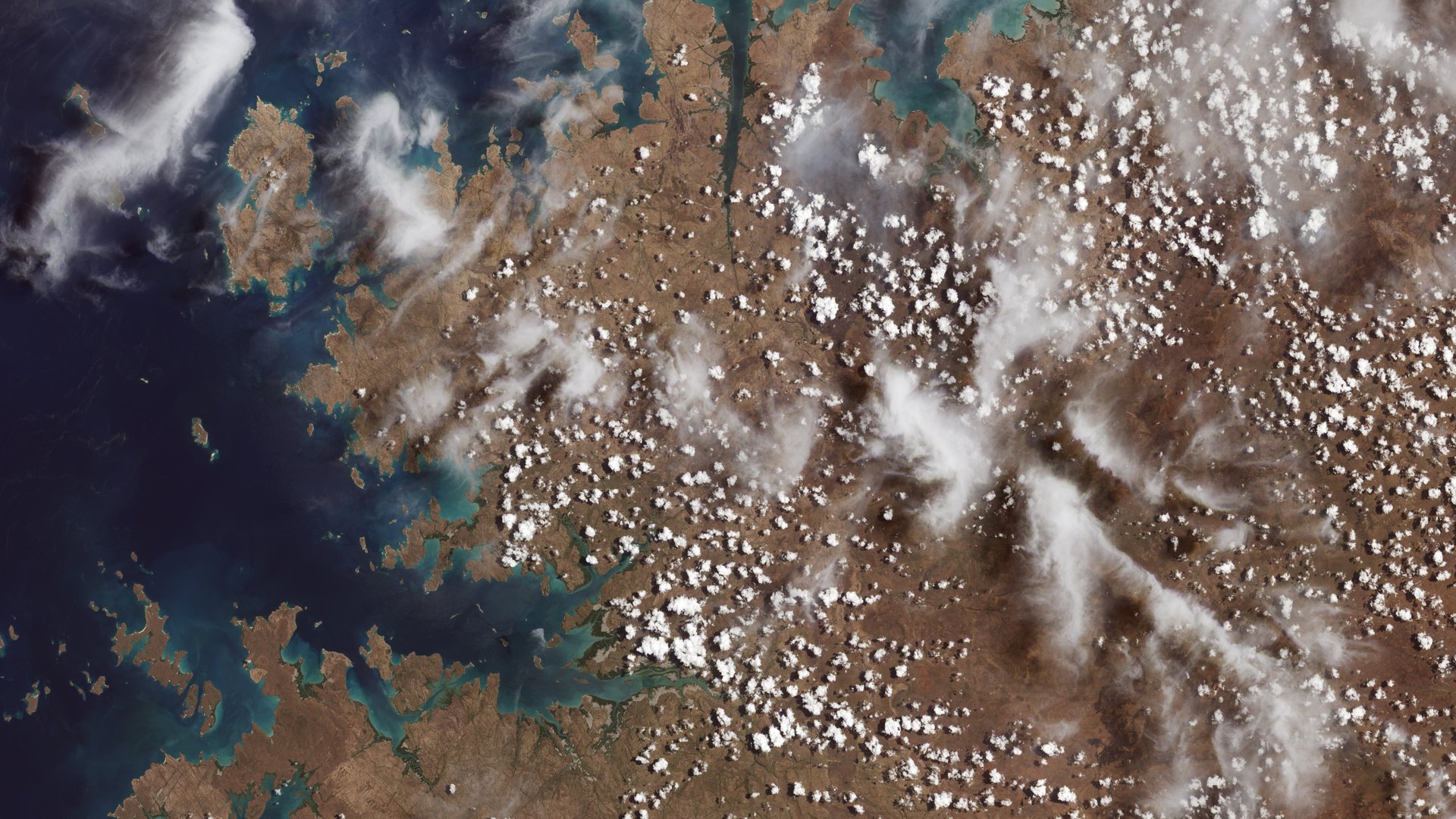
The nine photos, available for perusing online, capture Detroit with neighboring Lake St. Clair, the intersection of cities and beaches along a changing Florida coastline, Navajo Country in Arizona, the Himalayas, and the shorelines of Northern Australia.
The images are a small glimpse into the kind of data the satellite is collecting. The satellite detects visible, near-infrared light and thermal infrared data, the latter which measure Earth’s surface temperature and its changes. The improvements to Landsat 9 allows it to better detect subtle differences, including within densely-covered areas such as forests.
Amid a changing climate, the data collected provide scientists, city planners, farmers, and other stakeholders with information about crop health, irrigation use, water quality, wildfire severity, deforestation, glacial retreat, urban expansion, and more that can help them make better-informed choices for the future.
For instance, the images of Navajo Nation in the western US will aid with monitoring drought conditions and managing irrigation water. With only 85 rain gauges to cover more than 27,000 square miles, data there has been woefully incomplete; satellite imagery and climate models fill the gaps to help Navajo Nation monitor the drought severity, as NASA/USGS noted. In the Great Lakes, Landsat 9 captures swirls of green algae to help scientists and resource managers identify algal blooms early.
The latest images add to 50 years of space-based Earth observation. Since 1972, a partnership between NASA and the USGS, a bureau within the US Department of the Interior that studies the landscape of the US, has continuously had satellites in orbit taking pictures of Earth. These images have shown cities expanding into deserts or the changing colors depicting changing crops (the latter helps the US Department of Agriculture track crops over time).
In the future, USGS will operate Landsat 9 alongside Landsat 8, which will collect about 1,500 images of Earth’s surface every day, covering the globe every eight days.