How and where to see Friday’s total eclipse of the sun
Advice for seeing the solar eclipse on Friday (March 20) in northern Europe ranges from the exuberant (go to Svalbard) to the cautious (don’t even look at it).


Advice for seeing the solar eclipse on Friday (March 20) in northern Europe ranges from the exuberant (go to Svalbard) to the cautious (don’t even look at it).
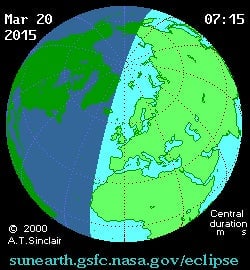
Both approaches have their merits. The eclipse’s line of “greatest duration” curves north and eastwards from below the tip of Greenland to the Arctic, passing through the Faroe Islands and Norway’s Svalbard archipelago. Iceland, Ireland, and the UK are just a few hundred miles from the point of both greatest duration and “greatest eclipse”—a measure of how complete the sun will be blocked out.
As the moon’s orbit takes it in front of the sun, casting a shadow on the Earth, a partial eclipse will be visible across North Africa, Europe and Northern Asia.
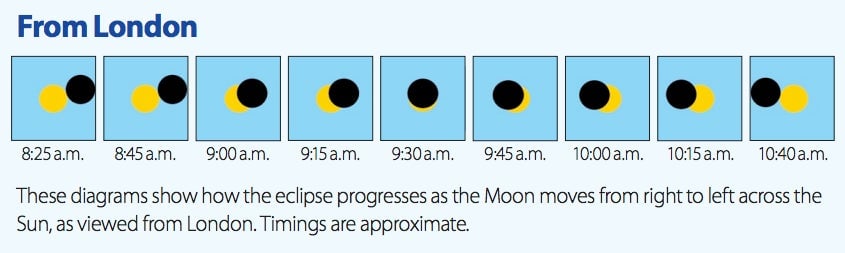
The UK’s Met Office created a useful map of places to see the eclipse in the UK. In Penzance, at the southernmost tip of Cornwall, at 9:23am local time there will be as much as a 90% eclipse. In Lerwick, in the Shetland Islands, a 98% eclipse should take place around 9:43. Watchers in London should be outside by 9:30 to get the maximum effect.
In all, the sun will be at least partially obscured for the better part of two hours. NASA cautions that the most important factor in getting a good view of the eclipse is not location, but the weather.
As we should all know by now, looking directly at the sun—even when it’s partly darkened by the moon—is dangerous. There are several ways of enjoying the eclipse, none of which involve staring upward with your eyes unprotected (and sunglasses won’t cut it). The Royal Astronomical Society’s booklet is full of ideas (pdf), from how to make a pinhole viewer to the best way to use a mirror, kitchen colander, or binoculars to project an image of the sun on any surface.
The last total eclipse could be seen from Australia in November 2012, according to NASA, which provides a large database of eclipse information. The next opportunity after this week will be in March 2016 in the Philippines. Europeans will have to wait until 2026 for another chance.
And the eclipse isn’t the only notable astronomical event this week. The day before, there will also be a “supermoon“—the moment when the earth and moon are as close together as possible, and when the latter may appear particularly large and red. The day of the eclipse is also the Spring equinox.