If capital is taking over the 21st century, what are we to do?
Thomas Piketty’s Capital in the Twenty-First Century has attracted plenty of debate over its thesis—that growing wealth inequality is an inevitable part of capitalism–but even those who find the arguments compelling aren’t necessarily on board with Piketty’s solution. Even he concedes that his proposal—new progressive taxes on net wealth—is a bit utopian. While a tax on wealth is direct, it’s politically fraught, hard to enforce, and depending on your preferred model of the economy, could slow growth.
But just as there is more than one way to skin a cat, there’s more than one way for society to push back against growing inequality. Commentators reacting to Piketty’s thesis have offered up a bevy of policy options they see as more feasible or with fewer unintended consequences.
1) Open the borders.

By intent and necessity, Piketty’s book is focused on wealthy countries, but we know well that emerging markets are only becoming more important to the global economy. Economist Suresh Naidu notes that “if we’re aiming for politically hopeless ideas, open migration is as least as good as the global wealth tax in the short run, and perhaps complementary.” More migration would redress global inequality by giving more earning power to migrants from poor countries, while lowering capital’s share of income in wealthy countries.
2) Get rid of some intellectual property protections.

One of the scary ideas in Piketty’s vision is the rise of a new class of rentiers who earn their money not by working but simply from the capital returns on their assets. One solution is to get rid of a major source of modern rents—patents on software and pharmaceuticals. The case against software patents has been made, even by software companies, as a way to stop wasteful patent trolling and unleash innovation. For medicines, that an Indian factory can make the same drugs far more cheaply than an American factory, with the only difference being patent protection, means there is already pressure on the current system. While drug companies say the research that leads to new cures wouldn’t be possible without restrictive patents, economists wonder if pure competition wouldn’t do the same job.
3) Cut taxes.

This one is actually stolen from Piketty himself, who responds to skeptics of his wealth-tax idea by saying that the US already has a wealth tax. It varies from locality to locality, but the average American real-estate owner pays an average property tax of 1.38% of a home’s value. Piketty thinks that merely turning this into a tax on “net” and not nominal capital would help reduce inequality:
[The United States] has a property tax which is a pretty big wealth tax. I would prefer it to be a progressive tax that was proportional and I would prefer it to be on net wealth rather than the gross value of real estate—if you take someone whose house is $500,000 and they have a mortgage liability of $490,000, his net wealth is $10,000, I would propose he would pay no property tax, no wealth tax. Right now he is paying as much property tax as someone with no mortgage who inherited his apartment 20 years ago. My premise is not to tax to destroy the wealth of the wealthy, it’s to increase the wealth of the bottom and the middle class.
Of course, the missing tax revenue would have to be made up for somehow—higher taxes, less public spending, more public borrowing—elsewhere.
4) Crack down on offshore tax havens.
Many objections to Piketty’s wealth tax include a reference to how hard it would be to tax wealth, because wealth is so very good at hiding in shell companies and secretive offshore trusts. But that’s a problem already: Perhaps $34 to $109 billion in US-owned financial assets are hidden from the tax man in Caribbean tax havens, just to avoid income on capital gains, a recent study found. The good news from that same study is that a push for tax information exchanges is cutting down on assets hidden overseas. But there’s lots more to be done on that front, whether it’s demanding public registration of the true owners of shell companies, or getting more countries to sign tax information exchange agreements.
5) Open up the city.

One wealthy countries manifest inequality is the high cost of living in large cities. This cost is partly a result of high demand to live there, but is also the more artificial product of zoning decisions, building codes and nostalgia that prevent the optimal utilization of space. Changing building codes to allow more development of affordable housing, taller buildings and fewer subsidies for cars would help alleviate inequality.
6) Wait for China’s labor costs to catch up.

One big reason wages have stagnated in the American middle class—thus widening the gap between them and the rich—is competition with cheaper labor in China and other countries. It has pushed many manufacturing jobs offshore, or forced US factories to automate faster than they might have otherwise. But wages won’t be low in China forever: Labor costs are already rising there, as low-wage jobs move to other places. It’s not inevitable, but some economists think that the trend could continue, as so-called “catch-up” growth spreads across the world—Africa, perhaps, is next. This growth lifts living standards and makes workers demand raises. On a globe without an obvious source of cheap labor, wages have to rise. Smarter trade rules might help accelerate this process.
7) Unleash antitrust.

Fewer monopolies, lower prices, less inequality—it’s all so simple, right? Economist Dean Baker specifically cites the telecom industry and its push toward consolidation, but there are good arguments that sectors from beer to tech to agriculture have consolidated in ways, sometimes subtle, that hamper economic growth and competition. Anti-trust rules, aggressively enforced, could improve life for customers, and by forcing companies to compete rather than just sit on their monopolistic laurels, would also lower profit margins for shareholders—tough luck, but good for equality.
8) Punish the financial sector.

A favorite among populists of all stripes. Pruning the banks isn’t easy, as the mixed experience of reformers after the worst financial crisis in most of our lifetimes showed. But the financial sector’s growing share of income in wealthy economies still has people on the left and right supporting policy ideas—from financial transaction taxes, to higher capital requirements, to limits on bank sizes—that would make the sector less profitable. That means less money going to annual trading bonuses, and presumably more money invested in the real economy.
9) Create more sovereign-wealth funds.

The key reason inequality tends to increase, Piketty says, is that investment returns (which go to the rich) will always exceed economic growth. But what if we give the public a share of those investment returns? One proposal from economist Tyler Cowen is the creation of government-run investment funds. These are already a common tool in countries with massive natural-resource wealth; they serve to diversify the national income stream and make it more sustainable. The US—which is no slouch on the natural resources front itself—could conceivably create a sovereign-wealth fund and share the dividends.
10) Massive social upheaval and bloody conflict.
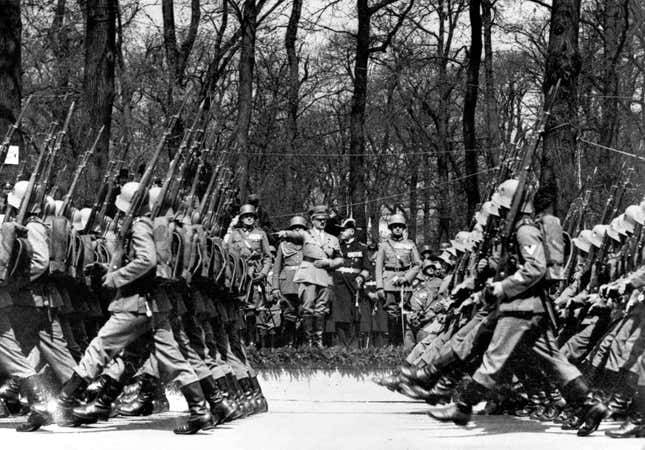

Not exactly ideal, but one of the most convincing empirical findings from Piketty’s research is that World War I, the Russian revolution and World War II were the great levelers of the 20th century, wiping out more than a century of capital accumulation and creating the conditions for more equitable growth in their wake. Continent-wide warfare may not be a pleasant prospect, but it’s probably a good deal easier to bring about than most of the solutions listed above. Why, there’s a handy little annexation going on in central Europe right about now.




