The Financial Times reports today that earlier this year Stephen Miller, president Trump’s hard-line advisor, had tried to convince the president to ban all Chinese students from entering the US.
It’s the latest point of tension between the two countries that has intensified in recent months. A Chinese national was arrested by US officials last week on suspicion he was spying for China while in the US on a student visa. President Trump has voiced concern that Chinese students are acting as spies, according to news reports. And of course, the US and China are currently engaged in a trade war.
Any change in the US’s treatment of Chinese students could have drastic effects on US colleges and universities. Chinese nationals make up the largest group of international students in the US. They account for roughly 30% of all foreign students. There were about 340,000 of them in July 2018.
About eight in 10 Chinese students are enrolled at institutions of higher education.
The students contribute to the US economy, bringing in both tuition and creating jobs. NAFSA estimated that for every seven international student enrolled, three jobs were created in the 2016-17 academic year.
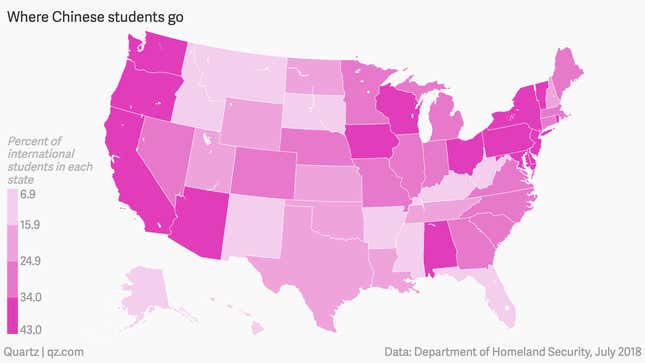
Most Chinese students live in coastal states such as California and New York. Though, certain states rely on China for students much more than others. Forty-two percent of international students in Vermont were from China in July 2018, followed by 40% for both Wisconsin and Oregon.
While a total ban of Chinese students is unlikely, the administration’s posturing has already contributed to a hostile climate against international students. Chinese students are increasingly choosing to return home after graduation, rather than staying in the US and contributing to the American economy.
